- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Cat. No.
Product Name
Unit Size
Order
Specification
Composition
Silica-coated iron oxide magnetic beads grafted with DADPA group on the surface
Bead Size
~1μm diameter; ~5μm diameter
Number of Beads
~ 1.68 x 109 beads/mg (1μm beads)
~ 5 x 107 beads /mg (5μm beads)
Surface Area
Stability
Short Term (<1 hour): pH 3-11; Long-Term: pH 4-10
Temperature: 4°C -140°C; Most organic solvents
Magnetization
~40-45 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Effective Density
2.5 g/ml
Formulation
20 mg/ml (1 mM ETDA, pH 7.0)
Functional Group Density
1μm Magnetic Beads
~200 μmole / g of Beads
5μm Magnetic Beads
~180 μmole / g of Beads
Storage
Store at 4°C, protected from light and free of moisture upon receipt
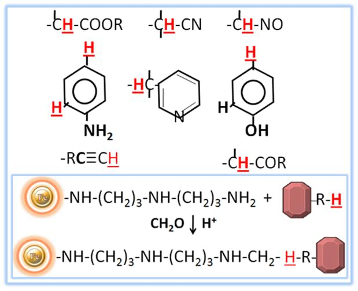
Immobilization using traditional procedures may be difficult for molecules lacking easily reactive functional groups. Certain medications, steroids, dyes, and other small chemical molecules, in particular, commonly have structures that lack appropriate reaction groups for immobilization. Other compounds have low-reactivity functional groups or are sterically inhibited. However, some of these compounds contain active (or replaceable) hydrogens that can be condensed using the Mannich method with formaldehyde and amine.
The Mannich reaction is defined as the condensation of formaldehyde (or another aldehyde) with ammonia and another molecule containing active hydrogen. Instead of ammonia, this reaction can be carried out with primary, secondary, or even amide amines. When diaminodipropylamine (DADPA) resin is used as the primary amine in this process, ligand immobilization occurs.
The BcMag™ Steroid/Drug/Dye Conjugation Protocol is a reliable and efficient method for conjugating small molecules that lack easily reactive functional groups, such as steroids, dyes, and medications. The protocol involves the use of DADPA-terminated magnetic beads, which are uniform, silica-based superparamagnetic beads coated with a high density of DADPA functional groups on the surface. The DADPA functional groups provide a site for the Mannich reaction to occur, allowing the immobilization of compounds that would be difficult or impossible to immobilize using present methods due to the absence or inaccessibility of easily reactive functional groups.
In the Mannich reaction, formaldehyde is condensed with an amine and another molecule containing active hydrogen. With the DADPA-terminated magnetic beads, the active hydrogen in the compounds to be immobilized reacts with formaldehyde and amine on the surface of the beads, leading to immobilization via Mannich reaction-induced coupling. This method has been shown to be highly efficient, and the resulting immobilized compounds have been used in various applications, such as drug screening, protein purification, and immunoassays.
●
High binding capacity
●
Fast, efficient coupling
●
Hydrophilic long-arm spacer minimizing steric hindrance and non-specific binding
Magnetic Beads Make Things Simple