- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Cat. No.
Product Name
Unit Size
Order
Specification
Composition
Silica-coated iron oxide magnetic beads grafted with DADPA group on the surface
Bead Size
~1μm diameter; ~5μm diameter
Number of Beads
~ 1.68 x 109 beads/mg (1μm beads)
~ 5 x 107 beads /mg (5μm beads)
Surface Area
Stability
Short Term (<1 hour): pH 3-11; Long-Term: pH 4-10
Temperature: 4°C -140°C; Most organic solvents
Magnetization
~40-45 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Effective Density
2.5 g/ml
Formulation
20 mg/ml (1 mM ETDA, pH 7.0)
Functional Group Density
1μm Magnetic Beads
~200 μmole / g of Beads
5μm Magnetic Beads
~180 μmole / g of Beads
Storage
Store at 4°C, protected from light and free of moisture upon receipt
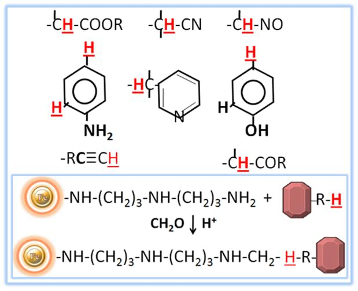
Sometimes it can be difficult to immobilize certain molecules using traditional procedures if they lack easily reactive functional groups or have low-reactivity functional groups or are sterically inhibited. However, the Mannich reaction can be used to immobilize these molecules by condensing formaldehyde and amine with a molecule that contains active hydrogen. This reaction can be carried out with primary, secondary, or amide amines instead of ammonia. By using DADPA resin as the primary amine in this process, ligand immobilization can occur.
To efficiently conjugate compounds such as steroids, dyes, and medications that lack easily reactive functional groups, the BcMag™ Steroid/Drug/Dye Conjugation Protocol uses DADPA-Terminated Magnetic Beads via the Mannich reaction-induced immobilization method. These magnetic beads are silica-based and superparamagnetic, with a high density of DADPA functional groups on the surface. This method provides a way to immobilize small molecules with active hydrogens that are difficult or impossible to immobilize using current methods.
●
High binding capacity
●
Fast, efficient coupling
●
Hydrophilic long-arm spacer minimizing steric hindrance and non-specific binding
Protocol (Carboxy-containing ligand conjugation)
●
The following protocol is an example for coupling amine-containing ligands to BcMag™ DADPA-terminated magnetic beads. This protocol can be scaled up and down accordingly. Titration is strongly advised to optimize the number of beads needed for each application.
●
The coupling buffer or ligand should not contain any amino (e.g., Tris) or formyl groups.
●
Coupling efficiency is very low for ligand-containing due to solution phase polymerization.
Materials Required
●
Coupling Buffer: 0.1 M MES, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 4.7
●
Wash Buffer: 0.1 M Tris, pH 8.0
●
Coupling Reagent: 37% formaldehyde
●
Magnetic Rack (for manual operation)
Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following Magnetic Racks:
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-01);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-02);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-03);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-04);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-96 for holding a 96 ELISA plate or PCR plate (Cat. No. MS-05).
A.
Sample Preparation
1.
Dissolve 1-10mg ligand in 1ml coupling buffer if soluble. If insoluble, dissolve it in 0.5 ml 100% Ethanol, then add 0.5 ml coupling buffer to make 50% Ethanol/buffer.
Note: If Ethanol is used for coupling, the magnetic beads must be washed with 50% Ethanol before adding the sample.
B.
Magnetic Beads Preparation
1.
Shake the bottle to completely resuspend the beads and transfer 30 mg Magnetic beads to a centrifuge tube.
2.
Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack. Remove the tube from the rack and resuspend the beads with 1 ml coupling buffer by vortex for 30 seconds.
3.
Repeat step 2 two times.
C.
Coupling
1.
Add sample from A1 and 100 μl coupling reagent to the washed magnetic beads, mix well and incubate at 38-60 ˚C for >48 hours with continuous rotation.
Note: The user should empirically determine the optimal coupling reaction times and temperatures.
2.
Note:
3.
Resuspend the beads in desired buffer containing 0.05% sodium azide and store them at 4°C.
D.
General Affinity Purification Protocol
1.
Transfer the optimal amount of the beads to a centrifuge tube. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
Note:
●
It is strongly recommended that a titration be performed to optimize the number of beads used for each application based on the amount of the target protein in the crude sample. Too many magnetic beads used will cause higher backgrounds, while too few beads used will cause lower yields. Each mg of conjugated magnetic beads typically binds to 1-20 μg of the target protein.
2.
Remove the tube and resuspend the beads with a 5-bed bead volume of PBS buffer by vortex for 30 seconds. Leave the tube at room temperature for 1-3 minutes. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
3.
Repeat step 2 two times
4.
Add washed beads to a crude sample containing the target protein and incubate at room temperature or desired temperature for 1-2 hours (Lower temperature require longer incubation time).
5.
6.
Elute the target protein by appropriate methods such as low pH (2-4), high pH (10-12), high salt, high temperature, affinity elution,or boiling in SDS-PAGE loading buffer.
Magnetic Beads Make Things Simple