- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Cat. No.
Product Name
Unit Size
Order
FW111
BcMag™ CDI-Activated Magnetic Beads Conjugation Buffer Kit
Kit Components
– Conjugation Buffer: 100 ml (100 mM, Sodium carbonate buffer, pH 9)
– Blocking Buffer: 20 ml (1 M Tris•HCl, pH 9)
– 10x Wash Buffer: 20ml (10x PBS, pH 7.2)
Each
Specification
Composition
Magnetic Bead grafted with CDI group on the surface
Number of Beads
~ 1.68 x 109 beads/mg (1μm beads)
~ 5 x 107 beads /mg (5μm beads)
Stability
Short Term (<1 hour): pH 3-11; Long-Term: pH 4-10
Temperature: 4°C -140°C; Most organic solvents
Magnetization
~40-45 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Formulation
Lyophilized Powder
Functional Group Density
1μm Magnetic Beads
~250 μmole / g of Beads
5μm Magnetic Beads
~200 μmole / g of Beads
Storage
Ship at room temperature. Store at 4°C upon receipt. Do not freeze
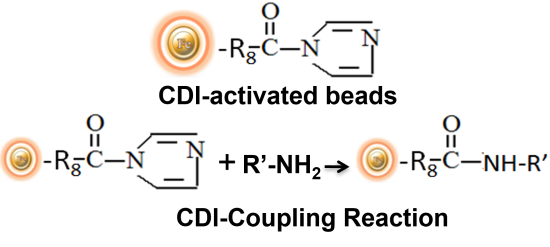
Introducing the innovative CDI-activated support for immobilizing amine-containing affinity ligands – a versatile alternative to traditional methods. This unique approach involves the reaction of the support with primary amine-containing ligands in an aqueous coupling buffer. During the process, the imidazole groups are lost, and carbamate linkages are formed. This coupling process takes place at a basic pH range of 8.5-10, which is slightly slower than the reductive amination coupling process with proteins. However, the reaction can also be carried out in an organic solvent, making it possible to couple water-insoluble ligands as well. The CDI-activated resins are particularly effective at immobilizing peptides and tiny chemical compounds.
Enter BcMag™ CDI-Activated Magnetic Beads – a carbonyldiimidazole affinity chromatography resin that has been expertly activated for covalent immobilization of N-nucleophiles and primary amine ligands at pH 9 to 11 in both aqueous and organic solvent conditions. What sets these beads apart is their unique ability to conjugate water-insoluble peptides and small organic molecules in an organic solvent. Ideal for conjugating large proteins and peptides, BcMag™ CDI-activated magnetic beads are a game-changer in the field of immobilization.
Conjugation Protocol
Note:
●
This protocol can be scaled up as needed. We strongly recommended titration to optimize the number of beads used for each application.
●
Avoid tris or other buffers containing primary amines or other nucleophiles because these will compete with the intended coupling reaction. But the wash or storage buffers can contain amino.
Materials required
●
Magnetic Rack (for manual operation)
Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following Magnetic Racks:
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-01);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-02);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-03);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-04);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-96 for holding a 96 ELISA plate or PCR plate (Cat. No. MS-05).
●
Coupling/Washing
1.
Soluble ligand coupling buffer: 0.1 M Carbonate buffer, pH 10
2.
Insoluble ligand coupling buffer: Dry acetone, dioxane, or dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)
●
Blocking Buffer: 100 mM Tris, pH 10
●
PBS buffer
A.
Ligand preparation
Note:
Coupling efficiencies to CDI-activated magnetic beads vary from ligand to ligand. The user should empirically optimize the concentration of the ligand. For protein, using 0.5-10 mg/ml. The ligand concentration should be at least 200 μmoles per ml for small peptides.
1.
Prepare 100 μl of protein solution (0.5-1mg/ml) or peptide solution (200 μmoles/ml) with coupling buffer. If samples have already been suspended in another buffer, dilute samples with an equal volume of coupling buffer.
B.
Beads Preparation
1.
Prepare 3% magnetic beads with acetone (30 mg/ml) and mix well.
Note: Store the unused beads in acetone solution at 4°C. It is stable for over a year.
2.
Transfer 100 μl (3mg) magnetic beads to a centrifuge tube.
3.
Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack. Remove the tube from the rack and resuspend the beads with 1 ml coupling buffer by vortex for 30 seconds.
4.
Repeat step 3 two times.
5.
Remove the supernatant, and the washed beads are ready for coupling.
Note: Once rehydrated using the coupling buffer, use the Bead as soon as possible due to the stability of the functional group.
C.
Coupling
1.
Add sample to the washed magnetic beads and incubate at room temperature overnight with continuous rotation.
Note: The user should optimize the incubation time.
2.
Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack. Remove the tube from the rack and resuspend the beads with 1 ml coupling buffer by vortex for 30 seconds.
3.
Repeat step 3 two times.
4.
Add 1ml of blocking buffer to the beads and incubate the reaction at room temperature for 4 hours or at 4 °C overnight with continuous rotation.
5.
Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack. Remove the tube from the rack and resuspend the beads with 1 ml PBS buffer by vortex for 30 seconds.
6.
Repeat step 5 for two times.
7.
Resuspend the beads in PBS buffer with 0.01% azide (w/v) to desired concentration and store at 4°C until use. Do not freeze.
D.
General Affinity Purification Protocol
Note:
●
This protocol is a general affinity purification procedure. Designing a universal protocol for all protein purification is impossible because no two proteins are precisely alike. The user should determine the optimal working conditions for purifying the individual target protein to obtain the best results.
●
We strongly recommended titration to optimize the number of beads used for each application based on the amount of the target protein in the crude sample. Too many magnetic beads used will cause higher backgrounds, while too few beads used will cause lower yields. Each mg of magnetic beads typically binds to 10-20 μg of the target protein.
1.
Transfer the optimal amount of the beads to a centrifuge tube. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
2.
Remove the tube and wash the beads with 5-bed volumes of PBS buffer by vortex for 30 seconds. Leave the tube at room temperature for 1-3 minutes. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
3.
Repeat step 2 two times.
4.
Add washed beads to the crude sample containing the target protein and incubate at room or desired temperature for 1-2 hours (Lower temperatures require longer incubation time).
Note: Strongly recommended to perform a titration to optimize incubation time. More prolonged incubation may cause higher background.
5.
Note: Adding a higher concentration of salts, nonionic detergent, and reducing agents may reduce the nonspecific background. For example, adding NaCl (up to 1-1.5 M), 0.1-0.5% nonionic detergents such as Triton X 100 or Tween 20, and a reducing reagent such as DTT or TCEP (we usually use 3mM ) to the washing buffer.
6.
Elute the target protein by appropriate methods such as low pH (2-4), high pH (10-12), high salt, high temperature, affinity elution, or boiling in an SDS-PAGE sample buffer.
Magnetic Beads Make Things Simple