- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Cat. No.
Product Name
Unit Size
Order
FB113
BcMag™ Carboxy-Terminated Magnetic Beads Conjugation Buffer Kit
Kit Components
Each
Specification
Composition
Magnetic beads grafted with a high density of carboxyl groups on the surface
Number of Beads
~ 1.68 x 109 beads/mg (1μm beads)
~ 5 x 107 beads /mg (5μm beads)
Stability
Short Term (<1 hour): pH 4-11; Long-Term: pH 4-10
Temperature: 4°C -140°C; Most organic solvents
Magnetization
~40-45 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Formulation
Lyophilized Powder
Functional Group Density
1μm Magnetic Beads
~200 μmole / g of Beads
5μm Magnetic Beads
~180 μmole / g of Beads
1μm Long-Arm Magnetic Beads
~160 μmole / g of Beads
5μm Long-Arm Magnetic Beads
~130 μmole / g of Beads
Storage
Store at 4°C upon receipt.
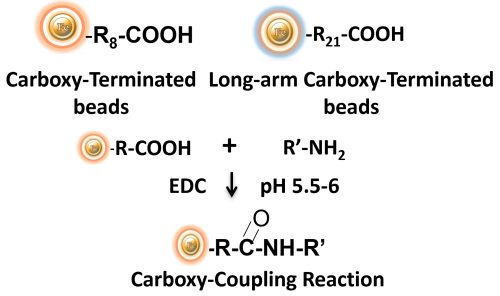
BcMag™ Carboxyl-Terminated Magnetic Beads are silica-based magnetic beads coated with a dense layer of carboxylic acid groups on the surface, ensuring uniformity. With a hydrophilic surface, these beads exhibit low nonspecific adsorption, great dispersion, and easy handling in various buffers. These high-density carboxylic acid groups enable the stable formation of amide bonds and covalent conjugation of ligands containing primary amines (as shown in Figure below). The hydrophilic surface of BcMag™ Carboxyl-Terminated Magnetic Beads also allows for excellent dispersion, low nonspecific adsorption, and easy handling in various buffers, making them ideal for conjugating larger proteins. For conjugating small peptides, BcMag™ Long-arm Carboxyl-terminated Magnetic Beads are recommended due to their long-arm hydrophilic linker, which reduces steric hindrance.
Protocol (Carboxy-containing ligand conjugation)
Note:
1.
This protocol can be scaled up as needed. We strongly recommended titration to optimize the number of beads used for each application.
2.
The coupling buffers should have minimal ionic strengths and contain no amino (e.g., Tris) or carboxyl groups (e.g., acetate, citrate). But the wash or storage buffers can have amino or carboxyl groups.
Materials Required
●
Magnetic Rack (for manual operation)
Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following Magnetic Racks:
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-01);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-02);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-03);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-04);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-96 for holding a 96 ELISA plate or PCR plate (Cat. No. MS-05).
●
Coupling Buffer: 10 mM potassium phosphate, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 5.5 or 0.1 M MES Buffer, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 4.5-5.5.
Note: For Long-arm carboxy-terminated magnetic beads, adjust NaCl concentration to 0.3-0.5 M (Final concentration) in coupling buffer.
●
EDC [1-ethyl-3 (3-dimethyaminopropyl) carbodiimide], Sigma, Cat. No. E7750
●
NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide), Sigma, Cat. No. 56480
●
Wash/Storage Buffer: 10 mM Tris base, 0.15 M NaCl, 0.1% (w/v) BSA, 1mM EDTA, 0.01% sodium azide, pH 7.5.
●
Blocking buffer: 1 M Glycine, pH 8.0
I.
Protocol (one-step coupling)
Note:
The one-step coupling is suitable for ligands that do not contain carboxylic acid groups since carboxylic acid groups may react with the EDC and cause polymerization of the ligand. Since this method is simple and generally yields higher, it is still the preferred coupling method. To compensate for the loss due to polymerization, add excess ligands in the coupling reaction. However, since this method is simple and generally gives higher yields, it is still the preferred coupling method.
A.
Magnetic Beads Preparation
1.
Combine 30 mg with 1 ml coupling buffer in a centrifuge tube and mix well by vortexing or pipetting.
2.
Insert the tube into a magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes until the supernatant becomes clear. Aspirate and discard the supernatant with a pipette while the tube remains in the rack.
3.
The beads are ready for coupling.
B.
Protein Coupling
1.
Prepare 1 ml of protein solution (0.5-1mg/ml) with coupling buffer and mix well with the above-washed beads.
2.
Freshly prepare 2% EDC solution with coupling buffer.
Note: use within 15 minutes of preparing.
3.
Add 100 μl of 2% EDC solution to the protein solution and mix well
4.
Incubate at room temperature overnight at room with good mixing (end-over-end).
C.
Remove uncoupled protein
1.
When the reaction is finished, place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
2.
Washing the beads with 5 ml Wash/storage buffer three times.
3.
Incubate the beads with 1ml of Blocking buffer at room temperature with good mixing (end-over-end) for 1-2 hours
4.
Washing the beads with 5 ml Wash/storage buffer three times
5.
Suspend the beads with the desired Wash/storage buffer volume and store them at 4º C.
II.
Protocol (two-step coupling)
Note:
Two-step protocol: This protocol is preferred for ligands that contain carboxyl groups or you have only limited amounts of ligand available.
A.
Magnetic beads preparation
1.
Combine 30 mg with 1 ml coupling buffer in a centrifuge tube and mix well by vortexing or pipetting.
2.
Insert the tube into a magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes until the supernatant becomes clear. Aspirate and discard the supernatant with a pipette while the tube remains in the rack.
3.
Freshly prepare 5% EDC and 5% NHS solutions with coupling buffer.
Note: use within 15 minutes of preparing.
4.
Add 500 μl of 5% EDC and 500 µl NHS to the beads and mix well.
5.
Incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes with good mixing (end-over-end).
6.
After incubation, insert the tube into a magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes until the supernatant becomes clear. Aspirate and discard the supernatant with a pipette while the tube remains in the rack.
7.
Washing beads with 5 ml cold coupling buffer three times.
8.
The beads are ready for coupling the ligands.
B.
Protein coupling
1.
Prepare 1 ml of protein solution (0.5-1mg/ml) with coupling buffer and mix with the above-washed beads.
2.
Incubate at room temperature overnight with good mixing (end-over-end).
C.
Remove uncoupled protein
1.
When the reaction is finished, place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
2.
Washing the beads with 5ml Wash/storage buffer three times.
3.
Incubate the beads with 1ml of Blocking buffer at room temperature with good mixing (end-over-end) for 1-2 hours.
4.
Washing the beads with 5ml Wash/storage buffer three times.
5.
Suspend the beads with the desired Wash/storage buffer volume and store them at 4º C.
III.
General affinity purification Protocol
Note:
●
This protocol is a general affinity purification procedure. Designing a universal protocol for all protein purification is impossible because no two proteins are precisely alike. To obtain the best results, each user must determine the optimal working conditions for the purification of the individual target protein.
●
We strongly recommended titration to optimize the number of beads used for each application based on the amount of the target protein in the crude sample. Too many magnetic beads used will cause higher backgrounds, while too few beads used will cause lower yields. Each mg of magnetic beads typically binds to10-20 μg of the target protein.
1.
Transfer the optimal amount of the beads to a centrifuge tube. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
2.
Remove the tube and wash the beads with 5-bed volumes of PBS buffer by vortex for 30 seconds. Leave the tube at room temperature for 1-3 minutes. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
3.
Repeat step 2 two times.
4.
Add washed beads to the crude sample containing the target protein and incubate at room or desired temperature for 1-2 hours (Lower temperatures require longer incubation time).
Note: Strongly recommended to perform a titration to optimize incubation time. More prolonged incubation may cause higher background.
5.
Note: Adding a higher concentration of salts, nonionic detergent, and reducing agents may reduce the nonspecific background. For example, adding NaCl (up to 1-1.5 M), 0.1-0.5% nonionic detergents such as Triton X 100 or Tween 20, and a reducing reagent such as DTT or TCEP (we usually use 3mM) to the washing buffer.
6.
Elute the target protein by appropriate methods such as low pH (2-4), high pH (10-12), high salt, high temperature, affinity elution, or boiling in an SDS-PAGE sample buffer.
Magnetic Beads Make Things Simple