- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Shipping conditions: At ambient temperature
Handling and Storage: Store the kit components according to the table Above on arrival.
Liquid (Supplied in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2 and 50% Glycerol.)
Shipping:
Shipped at ambient temperature (stable for at least 20 days at room temperature). Upon receipt, store nuclease magnetic Beads at -20°C. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
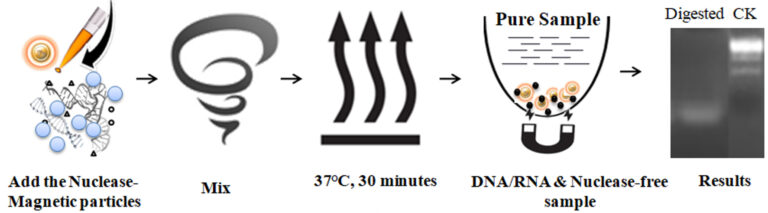
BcMag™ One-Step DNA & RNA Removal Kit uses endonuclease -immobilized magnetic beads to remove DNA and RNA from sample using a single step protocol. The recombinant endonuclease is encoded by the same gene of Merck Benzonase nuclease or TurboNuclease) of Serratia macescens produced in E. coli. This nuclease nonspecifically digests all kinds of DNA and RNA, including variants of single- and double-stranded, circular, linear, or supercoiled DNA and RNA to 5’-phosphorylated oligonucleotides of 2-8 bases in length and is free of protease activity. The nuclease immobilized magnetic bead can efficiently remove all the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) from protein solution with no endonuclease remaining in the solution due to the nuclease stably and covalently conjugated with the magnetic Beads.
An immobilized nuclease bead is ideal for removing nucleic acid contamination from purified proteins or other sample preparations.
●
Efficient one-tube and extraction-free protocol.
●
Ultrafast: Process 96 samples in less than 30 minutes with <10-second Hands-on Time.
●
Nuclease Recovered at the end of the reaction thereby can be reused.
●
Easy separation of the endonuclease from the protein sample.
●
Stability of the immobilized endonuclease increases.
●
Cost-effective: Eliminates columns, filters, laborious, organic reagents, and minimal plasticware required.
●
High throughput: Compatible with many different automated liquid handling systems.
A. Accessory equipment
Magnetic Rack
Item
Magnetic Rack for centrifuge tube
** Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following magnetic Racks
Source
• BcMag™ Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-01)
• BcMag™ Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-02)
• BcMag™ Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-03)
• BcMag™ Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-04)
Item
BcMag™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack.
Source
• BcMa™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack (side-pull) compatible with 96-well PCR plate and 96-well microplate or other compatible Racks (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-05)
Items
Magnetic Rack for centrifuge tube
** Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following magnetic Racks
Source
●
BcMag™ Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-01)
●
BcMag™ Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-02)
●
BcMag™ Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-03)
●
BcMag™ Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-04)
BcMag™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack
●
BcMa™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack (side-pull) compatible with 96-well PCR plate and 96-well microplate or other compatible Racks (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-05)
B. Procedure
●
Do not use buffers containing organic solvents.
●
Typically, the bead is added directly into any standard buffer at the desired amount of the beads based on the concentration of the contaminated nucleic acids. However, for the best results, users should reference the following table.
Working Conditions
Working Condition
Conditions
Dithiothreitol (DTT)
2-Mercaptoethanol
Temperature
Optimal Function
1-2 mM
0-95 mM
0-90 mM
37 °C
Functional Range
1-9 mM
>100 mM
0-50 °C
Inhibitory Action
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
0-20 mM
0-150 mM
pH
8.0-9.0
6.0-10.0
PMSF
1 mM
1M NaCl
Guanidine HCl
EDTA
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
100 mM reduces 75% enzyme activity
1 M reduces 75% enzyme activity
100 mM, completely inhibits enzyme activity
1mM reduces 30% enzyme activity.
100 mM can completely inactivate the enzyme activity
1.
Shake the bottle to completely resuspend the Magnetic beads until it is homogeneous.
IMPORTANT! It is important to mix the beads before dispensing. Do not allow the beads to sit for more than 2 minutes before dispensing. Resuspend the magnetic beads every 2 minutes.
2.
Add an appropriate amount of the magnetic beads to a protein sample containing nucleic acids.
3.
Mix the sample with beads for 1-2 minutes by slowly pipetting up and down 20-25 times or Vortex the sample for 2 minutes at 2000 rpm.
4.
Incubate at 37°C with continuous rotation for 30 minutes.
5.
Place the sample plate or tube on the magnetic Rack for 30 seconds or until the solution is clear.
(Option: centrifuge at 3500 rpm for 45 seconds)
6.
Transfer the supernatant to a clean plate /tube while the sample plate remains on the magnetic separation plate. The sample is ready for downstream applications.
1.
Lehman, I.R., Nussbaum A.L., The deoxyribonucleases of Escherichia coli. V. On the specificity of exonuclease I (phosphodiesterase), J. Biol. Chem., 239, 2628-2636, 1964.
2.
Werle, E., et al., Convenient single-step, one tube purification of PCR products for direct sequencing, Nucleic Acids Res., 22, 4354-4355, 1994.
3.
Nabavi S., Nazar R.N., Simplified one tube “megaprimer” polymerase chain reaction mutagenesis, Anal Biochem., 2, 346- 348, 2005.
4.
Rosamond, J., et al., Modulation of the action of the recBC enzyme of Escherichia coli K-12 by Ca2+, J. Biol. Chem., 254, 8646-8652, 1979.
5.
Sasaki, Y., Miyoshi, D. and Sugimoto, N., Regulation of DN nucleases by molecular crowding., Nucleic Acids Res., 35, 4086-4093, 2007.
6.
References 1. Lehman, I.R. and Nussbaum, A.L. (1964) J. Biol. Chem. 239, 2628. 2. Kusher, S.R. et al., (1971) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68, 824. 3. Kusher, S.R. et al., (1972) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 69, 1366. 4. Goldmark, P.J. and Linn, S. (1972) J. Biol. Chem. 247, 1849. 5. Rosamond, J. et al., (1979) J. Biol. Chem. 254, 8646.
Magnetic Beads Make Things Simple