- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Cat. No.
Product Name
Unit Size
Order
MMI101
BcMag™ Monomer Avidin Magnetic Beads
Kit components:
– 20 ml 1x Blocking / Elution Buffer
– 20 ml 1x Regeneration Buffer
– 30 ml 5x PBS Buffer
Kit
Specification
Beads Size
~ 2.5 μm diameter
Number of Beads
~ 1.47 x 108 beads/mg (2.5μm beads)
Magnetization
~ 40 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Stability
Short term: pH 3-11; Long term: pH 4-10
Binding Capacity
~ 1 mg biotinylated BSA / ml of Beads
Storage
Store at 4ºC upon receipt
Shipping conditions: At ambient temperature
Handling and Storage: Store the kit components according to the table above on arrival.
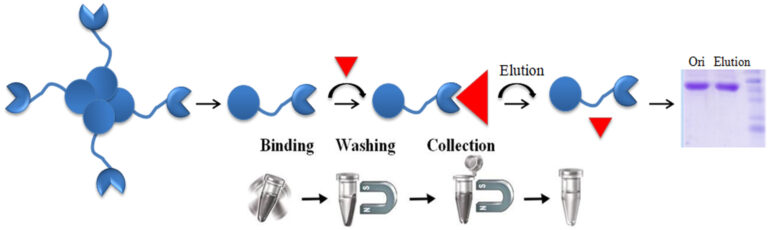
BcMag™ Monomer Avidin Magnetic Beads are highly uniform superparamagnetic microspheres coated with high purity density (>97%) avidin subunit monomer on the surface. Monomeric avidin, derived from the native tetrameric protein, retains the same biotin-binding specificity as native avidin, but its biotin-binding affinity dramatically decreases (kD=~10-8M). Therefore, the bound molecules can be easily eluted from the beads by mild elution conditions such as 2mM biotin instead of harsh elution reagents such as 8M guanidine or SDS detergent. The beads perfectly fit into applications such as immunoprecipitation, cell sorting, and rapid single-step capture of biotinylated molecules such as DNA, RNA, antibody, or protein from cell lysates or hybridization reactions.
The interaction between avidin (or streptavidin) and biotin exhibits one of the highest known non-covalent interactions). Avidin, streptavidin, monomeric avidin, and their analogs have become powerful tools for probes and affinity ligands for various applications in biochemical assays, diagnosis, affinity purification, and drug delivery.
1.
Quick, Easy, and one-step high-throughput procedures; eliminates columns or filters or laborious repeat pipetting or centrifugation
2.
High binding capacity and elute bound biotinylated molecules in mild conditions.
3.
Purifies biotinylated products under mild elution conditions
4.
Exhibits little nonspecific binding
5.
Scalable – Easily adjusts for sample size and automation
6.
Low cost – Up to half the price of competitive magnetic beads
7.
Beads can be reused at least five times
Buffer
●
1x PBS Buffer (0.1 M sodium phosphate, 0.15 M sodium chloride; pH 7)
●
1x Regeneration Buffer (0.1 M Glycine/HCl, pH 2.8)
●
1x Blocking/Elution Buffer (2 mM D-biotin in PBS)
Magnetic Rack (for manual operation)
Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following Magnetic Racks:
●
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-01);
●
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-02);
●
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-03);
●
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-04);
●
BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-96 for holding a 96 ELISA plate or PCR plate (Cat. No. MS-05).
The protocol can be adequately scaled up or down.
Note: Before purifying biotinylated proteins, peptides, and other molecules. The user should equilibrate all the reagents contained in the kit to room temperature and make 1x working solutions with double-distilled H2O.
1.
Gently shake the Magnetic Beads bottle until the magnetic beads are entirely suspended—transfer 50 µl beads to a fresh tube.
Note: Each user should empirically determine the optimal amount of beads to be used based on the amount of the biotinylated molecules in the crude sample. Too many magnetic beads will result in a higher background; too little will reduce the yield. We recommend 50 μl of the wholly suspended beads per 50 μg of biotinylated molecules.
2.
3.
Wash the beads with four bead volumes of 1x PBS buffer as described in step 2.
4.
Add three bead volumes of 1x Blocking / Elution Buffer, mix well by vortex, and incubate at room temperature for 5 minutes. Place the tube on the magnetic Rack for 1 minute. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the Rack.
5.
Add six bead volumes of 1x Regeneration Buffer, mix well by vortex, and place the tube on the magnetic Rack for 1 minute. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the Rack.
6.
Add four bead volumes of 1x PBS Buffer and wash the beads as described in step A.2. The beads are ready to use.
Note: Use the beads immediately, or binding capacity will dramatically reduce the binding capacity.
7.
Add biotinylated molecules-containing sample, mix well by pipetting and incubate at room temperature for 30-60 minutes with gentle rotation.
8.
9.
Add one bead volume of Blocking/Elution Buffer, mix well by pipetting several times, and incubate at room temperature for 5-10 minutes to elute the bound biotinylated molecule from the magnetic beads.
1.
Laitinen OH, Nordlund HR, Hytönen VP, Uotila ST, Marttila AT, Savolainen J, Airenne KJ, Livnah O, Bayer EA, Wilchek M, Kulomaa MS. Rational design of an active avidin monomer. J Biol Chem. 2003 Feb 7;278(6):4010-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205844200. Epub 2002 Nov 27. PMID: 12458212.
2.
Bayer EA, Wilchek M. biotin-binding proteins: overview and prospects. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:49-51. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)84258-i. PMID: 2201883.
3.
Hirsch JD, Eslamizar L, Filanoski BJ, Malekzadeh N, Haugland RP, Beechem JM, Haugland RP. Easily reversible desthiobiotin binding to streptavidin, avidin, and other biotin-binding proteins: uses for protein labeling, detection, and isolation. Anal Biochem. 2002 Sep 15;308(2):343-57. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(02)00201-4. PMID: 12419349.
Magnetic Beads Make Things Simple