- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Cat. No.
Product Name
Unit Size
Order
MG101
BcMag™ GST-tagged Protein Purification Kit
Kit components:
– 2 ml BcMag™ Glutathione magnetic beads
– 12 ml 10x Binding/Washing Buffer
– 4 ml 2x Elution Buffer
– 0.3 g Glutathione (Reduced)
Each
Specification
Composition
Magnetic microsphere immobilized with Glutathione
Magnetization
~60 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Effective Density
2.5 g/ml
Concentration
50 mg/ml (1x PBS)
Binding Capacity
>2mg GST /ml of Beads
Storage
Store at 4ºC upon receipt
Shipping conditions: At ambient temperature
Handling and Storage: Store the kit at 4ºC on arrival.
BcMag™ GST-Tagged protein purification magnetic beads are magnetic microspheres covalently immobilized with a high density of Glutathione. The microspheres combine all the advantages of affinity protein purification (low costs, simplicity, high specificity, and capacity) and magnetic properties to perform efficient manual or automatic quick high-throughput purification. It is specially designed for the capture and purification of GST-tagged proteins from various sample types.
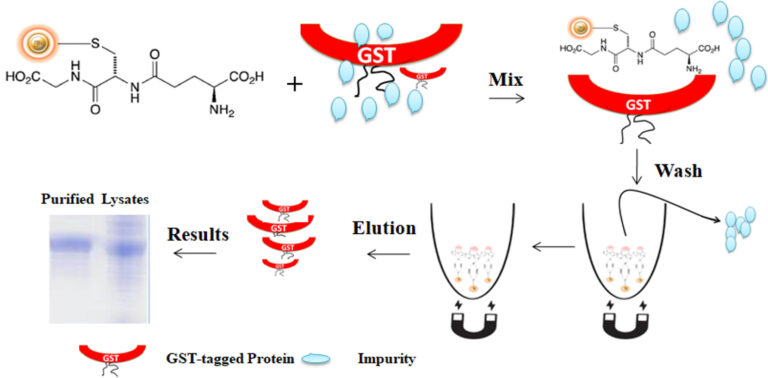
The purification with magnetic microparticles is straightforward (Fig.1). Mix the microparticles with the cell lysates and incubate them with continuous rotation for a sufficient time. The beads remain suspended in the sample solution during mixing, allowing the GST-tagged protein to bind to the immobilized ligand. After incubation, the beads are collected and separated from the sample using a magnet rack. Then the ultrapure GST-tagged recombinant proteins are eluted by excess reduced Glutathione.
●
Quick, Easy, and one-step high-throughput procedure; eliminates columns or filters or a laborious repeat of pipetting or centrifugation.
●
Stable covalent bond with minimal ligand leakage
●
High binding capacity, very low nonspecific binding
●
Scalable – Easily adjusts for sample size and automation
●
Reproducible results
●
Investigating protein structure and function
●
Preparing recombinant proteins for X-ray crystallography
●
Ideal for study of protein interactions with protein or DNA
●
Immunization to raise antibodies against a protein of interest
●
Effective screening protein expression even with crude cell lysates
●
Microscale purification of GST-tagged proteins
Glutathione-S-transferase (GST) is a highly soluble and stable 26 kDa enzyme that catalyzes the protective mechanisms of Glutathione (GSH). Many eukaryotic proteins are produced as inclusion bodies (insoluble aggregated protein), a malfunctioning protein caused by misfolding, in prokaryotic expression systems such as E. coli. It is usually painful to refold the inclusion body into a functional protein. GST is widely used as a fusion partner that promotes greater expression and solubility of the desired protein by taking advantage of its high stability and solubility to overcome this problem. Moreover, GST has a high affinity toward reduced Glutathione, its natural substrate. Therefore, GST as an affinity tag becomes a versatile tool for single-step purification of active recombinant production in a prokaryotic expression system.
Glutathione is a short peptide (Glu-Cys-Gly) that displays a high affinity toward glutathione S-transferase (GST). When the Glutathione is immobilized in a chromatography matrix such as beaded agarose or magnetic beads, the matrix can precisely capture GST-tagged protein via the affinity interaction. The GST tag can be fused to either the C- or N-terminus of a protein by inserting DNA sequence coding for the protein of interest into commercial expression vectors. The protein of interest can be cleaved off the GST tag by site-specific protease if desired. The protease site can be engineered between GST-tag and the protein of interest.
Currently, Glutathione is mainly immobilized to the traditional affinity chromatography matrices such as agarose resin or column. These solid matrices make the purification process tedious, time-consuming, unable to handle very tiny samples, and challenging to adapt to the automation system. Bioclone introduces a powerful magnetic beads-based GST–tagged protein system to overcome these problems.
1.
Frangioni, J.V. and Neel, B.G. (1993). Solubilization and purification of enzymatically active glutathione s-transferase (pGEX) fusion proteins. Anal Biochem 210:179-87.
2.
Simons, P.C. and VanderJagt, D.L. (1977). Purification of glutathione S-transferases for human liver by glutathione-affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem 82:334-41.
Magnetic Beads Make Things Simple