- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Cat. No.
Product Name
Unit Size
Order
Specification
Composition
Silica-enclosed magnetic beads grafted with m-aminophenyl boronic acid
Bead Size
5μm diameter
Magnetization
~40 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Effective Density
2.5 g/ml
Formulation
Lyophilized Powder
Binding Capacity
~ 2μmol boronate/mg
Storage
Upon receipt, store at 4°C
Shipping conditions: At ambient temperature
Handling and Storage: Store the kit components according to the table above on arrival.
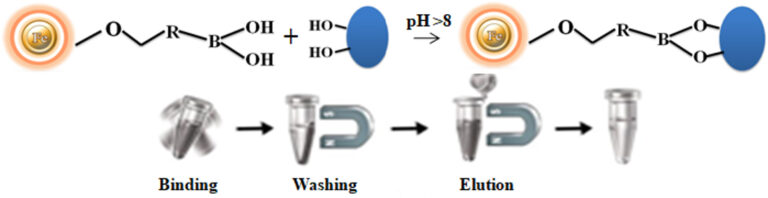
Affinity purifications are popular tools for the separation of biological compounds. Among them, boronate affinity chromatography is unique because the ligand (m-aminophenyl boronic acid) specifically and reversibly binds the vicinal diol of cis-diol-containing compounds at pH 8-9 and dissociates at pH 3-4 or addition of sorbitol. The boronate affinity resin is a powerful tool for efficiently enriching cis-diol-containing compounds such as alcohols, nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, and enzymes from complex samples such as human serum. Although current boronate affinity-based different chromatography matrices such as columns are available, their procedures are tedious, time-consuming, and unable to handle very tiny samples such as cancer-cell targeting and single-cell analysis. We developed a novel, efficient magnetic affinity system to overcome these limitations.
The affinity purification protocol is straightforward –
1.
Add the beads directly to the sample.
2.
3.
Magnetic separation of the beads from the sample.
4.
Wash to remove the nonspecific binding molecules.
5.
Elute the target molecules. The easy-to-use magnetic beads significantly improve results over the standard drip column and batch methodologies with minimum samples.
●
Simple protocol and Easy to use
●
Low nonspecific Binding
●
High binding capacity and elute bound vicinal diol group containing molecules in mile conditions.
●
Easy to use
●
Reliable and reproducible results
●
Cost-effective: Eliminates columns, filters, and laborious repeat pipetting
●
High-throughput: Compatible with many different automated liquid handling systems
Materials Required by the User
●
Binding/Wash Buffer: 50 mM HEPES, pH 8.5
Note: It may increase the binding capacity for some glycoproteins by adding 20–50 mM Mg2+ to the binding buffer. However, it may cause higher nonspecific Binding. We recommended performing a titration to optimize the concentration of Mg2+.
●
Elution Buffer:100 mM sorbitol, 50 mM HEPES, pH 8.5
●
Magnetic Rack
Item
Magnetic Rack for centrifuge tube
** Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following magnetic Racks
Source
• BcMag™ Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-01)
• BcMag™ Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-02)
• BcMag™ Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-03)
• BcMag™ Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-04)
Item
BcMag™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack.
Source
• BcMa™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack (side-pull) compatible with 96-well PCR plate and 96-well microplate or other compatible Racks (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-05)
Item
Adjustable Single and Multichannel Pipettes
Items
Magnetic Rack for centrifuge tube
** Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following magnetic Racks
Source
●
BcMag™ Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-01)
●
BcMag™ Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-02)
●
BcMag™ Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-03)
●
BcMag™ Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-04)
BcMag™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack
●
BcMa™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack (side-pull) compatible with 96-well PCR plate and 96-well microplate or other compatible Racks (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-05)
Adjustable Single and Multichannel Pipettes
Procedure
! Important !
●
The following protocol is an example of the purification of glycoprotein. We recommended performing a titration to optimize the amount of Beads used for each application. This protocol can be scaled up and down accordingly.
●
Do not use buffers containing organic solvents.
A.
Magnetic Beads preparation
1.
Resuspend the BcMag Magnetic Beads with Binding/Washing buffer to make 50mg/ml.
Note: It is essential to mix the beads before dispensing. Do not allow the beads to sit for more than 2 minutes before dispensing. Resuspend the magnetic beads every 2 minutes.
2.
Transfer desired amount of magnetic Beads to a tube. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
3.
Remove the tube and resuspend the Beads thoroughly with 10x Binding/Wash Buffer volumes. Leave the tube at room temperature for 2-3 minutes. Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
4.
Repeat step 3 once.
5.
Remove the tube from the rack and resuspend the Beads thoroughly with 10x Binding/Wash Buffer volumes. Place the tube on a magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
6.
Repeat step 5 once.
7.
Resuspend the Beads thoroughly with 1x volumes of Binding/Wash Buffer.
B.
Sample Binding/Washing
1.
Dilute sample with 15 x volumes of Binding/Wash Buffer.
2.
Add washed magnetic Beads to the diluted sample, mix Beads well with a pipette and leave them at room temperature for 10 minutes with gentle shaking.
3.
Place the tube on a magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes. Remove the supernatant while the tube remains on the rack.
4.
Remove the tube from the rack and wash the Beads with 15 x Binding/Wash Buffer volumes.
5.
Repeat step 3 until the absorbance at 280 nm reaches 0.001.
6.
Resuspend the Beads thoroughly with 1x volumes of Binding/Wash Buffer.
C.
Elution
1.
Remove the tube from the rack.
2.
Resuspend the Beads with 10-20 μl Elution Buffer and elute the target biomolecules by pipetting up and down 20-30 times.
3.
Place the tube on the magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes and transfer the supernatant containing the eluted protein to a new tube.
D.
Troubleshooting
Problem
Low yield
Probable Cause
The pH in the binding buffer or sample is not within 8.0–8.5.
Suggestion
Check the binding and sample pH to make sure it falls within 8.0–8.5
Problem
Non-Binding
Probable Cause
Some specific glycosylated proteins are poorly binding to the Beads.
Suggestion
Problem
Nonspecific Binding
Probable Cause
Suggestion
Problem
Probable Cause
Suggestion
Low yield
The pH in the binding buffer or sample is not within 8.0–8.5.
Check the binding and sample pH to make sure it falls within 8.0–8.5
Non-Binding
Some specific glycosylated proteins are poorly binding to the Beads.
Nonspecific Binding
1.
Herold DA, Boyd JC, Bruns DE, Emerson JC, Burns KG, Bray RE, Vandenhoff GE, Freedlender AE, Fortier GA, Pohl SL, et al. Measurement of glycosylated hemoglobins using boronate affinity chromatography. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1983 Nov-Dec;13(6):482-8. PMID: 6660832.
2.
Akshay Srivastava, Akhilesh Kumar Shakya, Ashok Kumar, Boronate affinity chromatography of cells and biomacromolecules using cryogel matrices, Enzyme and Microbial Technology,Volume 51, Issues 6–7,2012,Pages 373-381,ISSN 0141-0229
3.
Li D, Chen Y, Liu Z. Boronate affinity materials for separation and molecular recognition: structure, properties and applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2015 Nov 21;44(22):8097-123. doi: 10.1039/c5cs00013k. Epub 2015 Sep 17. PMID: 26377373
4.
Watanabe T, Momose I. [Boronic Acid as a Promising Class of Chemical Entity for Development of Clinical Medicine for Targeted Therapy of Cancer]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022;142(2):145-153. Japanese. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.21-00173-3. PMID: 35110451.
5.
Chen J, Hao L, Hu J, Zhu K, Li Y, Xiong S, Huang X, Xiong Y, Tang BZ. A Universal Boronate-Affinity Crosslinking-Amplified Dynamic Light Scattering Immunoassay for Point-of-Care Glycoprotein Detection. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022 Feb 7;61(7):e202112031. doi: 10.1002/anie.202112031. Epub 2021 Dec 23. PMID: 34881816.
Magnetic Beads Make Things Simple