- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Cat. No.
Product Name
Unit Size
Order
FD105
BcMag™ Hydrazide-Terminated Magnetic Beads Conjugation Buffer Kit
Kit Components
– 10x coupling Buffer: 25 ml 1M M sodium acetate, pH 5.6
– 5 x Wash Buffer: 50 ml 5M NaCl
Each
Specification
Composition
Magnetic Bead grafted with hydrazide group on the surface
Number of Beads
~ 1.68 x 109 beads/mg (1μm beads)
~ 5 x 107 beads /mg (5μm beads)
Stability
Short Term (<1 hour): pH 3-11; Long-Term: pH 4-10
Temperature: 4°C -140°C; Most organic solvents
Magnetization
~40-45 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Formulation
Lyophilized Powder
Functional Group Density
1μm Magnetic Beads
~200 μmole / g of Beads
5μm Magnetic Beads
~180 μmole / g of Beads
Storage
Ship at room temperature. Store at 4°C upon receipt. Do not freeze.
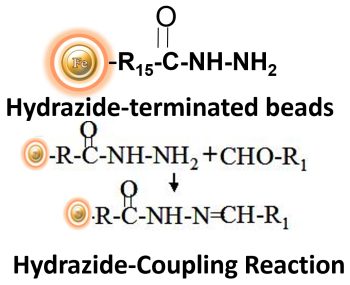
BcMag™ Hydrazide-Terminated Magnetic Beads are magnetic beads with a uniform structure, coated with a high density of hydrazide functional groups on their surface. This hydrazide chemistry is useful for labeling, immobilizing, or conjugating glycoproteins through glycosylation sites that are often located far from the critical binding sites, which need to be preserved (such as in most polyclonal antibodies). By coupling antibodies in this way, the heavy chains in the Fc portion of the molecule are selectively targeted, helping to preserve the antigen binding activity of the Fv regions. At a pH range of 5 to 7, hydrazide-terminated supports and compounds can react with oxidized carbohydrate carbonyls, resulting in the formation of hydrazone linkages (as shown in Figure below). These hydrazide beads are suitable for conjugating larger glycoproteins, glycolipids, carbohydrates, or other ligands. Additionally, the hydrophilic surface of the beads ensures low levels of nonspecific adsorption, excellent dispersion, and easy handling in various buffer solutions.
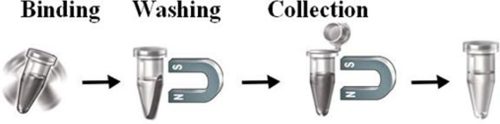
The Beads work perfectly as affinity resin for affinity purification to refine molecules, cells, and parts of cells into purified fractions. After conjugation with ligands, add the beads to a sample containing the target molecules, then mix, incubate, wash and elute the target molecules.
●
Specific immobilization – the hydrazide-activated beads bind exclusively to pure glycoproteins containing sugar groups that have been gently oxidized with periodate (e.g., sialic acid).
●
Stable covalent bond with low levels of ligand leakage
●
Maintains antibody function – immobilizes IgG via the Fc region, leaving both antigen binding sites available for target capture
●
Low nonspecific binding
●
High capacity—Immobilize 15-20μg antibody/mg beads
Immobilization Protocol
Note:
●
This protocol can be scaled up as needed. We strongly recommended titration to optimize the number of beads used for each application.
●
Avoid tris or other buffers containing primary amines because these will compete with the intended coupling reaction.
Materials Required
●
Magnetic Rack (for manual operation)
Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following Magnetic Racks:
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-01);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-02);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-03);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-04);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-96 for holding a 96 ELISA plate or PCR plate (Cat. No. MS-05).
●
Coupling Buffer: 0.1 M sodium phosphate, pH 7.0
●
●
Washing Buffer: 1M NaCl
●
PBS
Ligand Coupling
A.
Beads Preparation
1.
Weight 30 mg beads and add them into a 1.5 ml centrifuge tube.
2.
Add 1 ml coupling buffer and resuspend the beads very well by vortexing or pipetting.
3.
Insert the tube into a magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes until the supernatant becomes clear. Aspirate and discard the supernatant with a pipette while the tube remains in the rack.
4.
The beads are ready for coupling.
B.
Oxidation of Glycoprotein or other ligands
Note: The reaction is light sensitive and should be performed in the dark.
1.
Dissolve or dilute 0.5-10 mg glycoprotein or other ligands in 1 ml coupling buffer.
Note: If the protein or other ligands is already suspended in other buffers, perform a buffer exchange by dialysis or a desalting column.
2.
Add the protein or other ligands solution to an amber vial containing 2 mg sodium meta-periodate (final concentration10mM). Swirl gently to dissolve the oxidizing agent.
3.
Incubate the sample in the dark at room temperature for 45 minutes with good mixing (end-over-end).
C.
Conjugation
1.
Add the oxidized protein or other ligands solution to the prepared magnetic beads from Step A4 and mix well by vortexing or pipetting.
Note: Coupling efficiency depends on the structure and the size of the target glycoprotein or other ligands. The user should empirically optimize the ratio of the protein to the beads.
2.
Incubate the reaction in the dark at room temperature overnight with good mixing (en-over-end).
3.
Insert the tube into a magnetic rack for 1-3 minutes until the supernatant becomes clear. Aspirate and discard the supernatant with a pipette while the tube remains in the rack. Remove the tube from the rack and resuspend the beads with 5 ml Coupling Buffer by vortex or pipette.
4.
Repeat steps 3 for three times.
5.
Resuspend the beads in PBS buffer with 0.01% azide (w/v) to desired concentration and store at 4°C until use. Do not freeze.
Get the Latest News and Updates by Email
6393 Nancy Ridge Dr. Suite A
San Diego, CA 92121 USA
Fax: +1-858-909-0057
Get the Latest News and Updates by Email
© 2023 Bioclone Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Magnetic Beads Make Things Simple