- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Specification
Composition
Magnetic beads are modified with our proprietary chemistry.
Stability
Short Term (<1 hour): pH 4-11; Long-Term: pH 4-10
Temperature: 4°C -140°C; Most organic solvents
Magnetization
~40-45 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Formulation
100 mg / ml in 0.2 M Sodium phosphate, pH7.5, 0.3 M NaCl
Binding Capacity
~1500 pmol biotin/ml beads
Storage
Ship at room temperature, Store at 4°C upon receipt.
Biotin, also referred to as vitamin H, is a small molecule that is not commonly found in biological samples. It has a remarkable binding affinity for avidin (Ka=10^15) and streptavidin (Ka=10^14), making biotinylated molecules such as proteins or other molecules very useful for non-radioactive detection and purification of target molecules.
Biotinylation is a process used to attach biotin covalently to proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, or other molecules using enzymatic or chemical methods. This creates a biotinylated molecule with biotin attached to it. However, a certain amount of free biotin may remain in the sample after biotinylation, which can cause non-specific binding and result in background noise. Therefore, it is crucial to remove free biotin from the sample for successful downstream applications.
In order to eliminate any excess biotin in a sample, conventional techniques like dialysis or spin columns are often utilized. Unfortunately, these methods have some drawbacks, including loss of the sample due to protein precipitation, multiple buffer exchanges, transfer steps, lengthy protocols, and difficulty with low volume samples or high-throughput automation.
To overcome these challenges, a new and efficient biotin removal system has been developed.
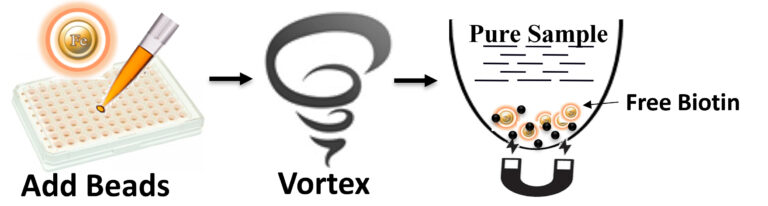
BcMag™ One-Step Free Biotin Removal Kit uses magnetic beads modified with proprietary chemistry to remove free biotin from sample. The beads can quickly and efficiently remove free biotin from ultra-low volumes of protein/ peptide or DNA/RNA solutions. The beads enable 96 samples to be processed simultaneously in less than 10 minutes.
The beads allow rapid and efficient removal of free biotin from the sample. The procedure is straightforward.
1.
Add the beads directly to the sample.
2.
Pipette or vortex to capture the free Biotin.
3.
Magnetic separation of the beads from the protein, or DNA/RNA solution, while the protein or DNA/RNA remains in the solution.
The easy-to-use magnetic beads significantly improve results over the standard drip column and batch methodologies with minimum protein loss (<10%). Since only a small volume of magnetic beads is used, the final protein concentration of the sample is not significantly decreased.
●
Simple protocol: No liquid transfer, One-tube, One-step, and one-minute protocol
●
Easy-to-use
●
Reliable and reproducible results with exceptional >90% recovery for protein (>6 kDa, aprotinin) or DNA/RNA (>25mer dsDNA)
●
Effective Cleanup: Remove 95% free Biotin
●
Cost-effective: Eliminates columns, filters, and laborious repeat pipetting
●
High throughput: Compatible with many different automated liquid handling systems
Materials Required by the User
A. Equipment
●
Magnetic Rack (for manual operation)
Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following Magnetic Racks:
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-01);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-02);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-03);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Cat. No. MS-04);
– BcMag™ Magnetic Rack-96 for holding a 96 ELISA plate or PCR plate (Cat. No. MS-05).
For larger scale purification, Ceramic magnets Block for large scale purification ( 6 in x 4 in x 1 in block ferrite magnet, Applied Magnets, Cat. No. CERAMIC-B8).
●
Corning 430825 cell culture flask for large-scale purification (Cole-Parmer, Cat. No. EW-01936-22)
●
Mini BlotBoy 3D Rocker, fixed speed, small 10″ x 7.5″ platform w/ flat mat (Benchmark Scientific, Inc. Cat. No. B3D1008) or compatible
Procedure
The following protocol is an example. The beads and sample volume can be rational Scale-up (or down). Do not use buffers containing organic solvents.
1.
Shake the bottle to resuspend the Magnetic beads until it is homogeneous entirely.
2.
Add an appropriate amount of the magnetic beads to the sample containing free biotin.
! IMPORTANT ! Users need to optimize the beads and free biotins ratio based on the binding capacity (~1500 pmol biotin/ml beads **). ** Binding capacity assay condition: Mix with 10 µl magnetic beads (100 mg/ml) with 100 µl protein sample (1:400 dilution of Human serum) containing biotins in 0.1M Sodium phosphate, 0.15M NaCl, pH7.5 buffer, and vortex at 2000 rpm for 5 minutes)
3.
Mix the sample with beads for 1-2 minutes by slowly pipetting up and down 20-25 times or vortex for 5 minutes at 2000 rpm for PCR plates or 800 rpm for microplates.
4.
Place the sample plate or tube on the magnetic separation plate for 30 seconds or until the solution is clear.
5.
Transfer the supernatant to a clean plate/tube while the sample plate remains on the magnetic separation plate. The sample is ready for downstream applications.
Troubleshooting
Problem
Low Protein Recovery
Probable Cause
Vortexing time is too long.
Suggestion
If using other digital vortex mixers, the vortex condition such as speed and time has to be optimized.
Problem
Low Protein Recovery
Probable Cause
Using too many magnetic beads
Suggestion
Completely resuspend the magnetic beads and reduce the amounts of the beads.
Problem
Failure to remove biotin.
Probable Cause
Used inappropriate tubes or plates
Suggestion
Ensure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of the Tubes or well of the plate is ≥2.5mm.
Problem
Failure to remove biotin.
Probable Cause
Suggestion
Problem
Probable Cause
Suggestion
Low Protein Recovery
Vortexing time is too long.
If using other digital vortex mixers, the vortex condition such as speed and time has to be optimized.
Using too many magnetic beads
Completely resuspend the magnetic beads and reduce the amounts of the beads.
Failure to remove biotin.
Used inappropriate tubes or plates
Ensure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of the Tubes or well of the plate is ≥2.5mm.
Get the Latest News and Updates by Email
6393 Nancy Ridge Dr. Suite A
San Diego, CA 92121 USA
Fax: +1-858-909-0057
Get the Latest News and Updates by Email
© 2023 Bioclone Inc. All Rights Reserved.