- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Fluorescent dyes, also called reactive dyes or fluorophores, are natural or synthetic compounds that absorb light and re-emit it at a longer wavelength. Due to their unique advantages, versatility, sensitivity, and quantitative capabilities, fluorescent dyes are widely used to label DNA/RNA as probes. End-labeling, nick-translation, and random primer production can all be used to label DNA/RNA molecules. The labeled DNA/RNA probes are widely used in molecular biology procedures such as gene library screening, identifying nucleotide sequences with blotting methods, and gene technologies such as nucleic acid and tissue microarrays. They can also be used to purify interacting molecules such as DNA binding proteins. DNA probes can be employed in environmental or health research to detect specific genes and bacteria in ambient or pathological materials via in-situ hybridization. After a fluorescent labeling reaction, removing excess or unreacted fluorescent dyes from the final labeling solution is often necessary since it interferes with many downstream applications. Removing fluorescent dyes is usually accomplished by spin columns, gel filtration, gravity-flow columns, and dialysis. However, those traditional methods present many problems, including time-consuming and labor-intensive processes, poor recovery of protein, peptides, or nucleic acids, and the challenge of adapting to automation. For this reason, we introduce a novel one-step dye removal system.
BcMag™ One-Step DNA Fluorescent Labeling Cleanup Kit has specially formulated resin with proprietary surface chemistry. It removes the excess free (non-conjugated) fluorescent dyes, primer, dimer, adapter, salt, detergent, labeled dNTPs, dNTPs, and enzymes from the finished labeling reaction. The protocol is not only straightforward but also very flexible in removing different size DNA fragments by adjusting processing time, buffer pH, and detergent concentration (table1). Compared with the dye removal columns, the resin can quickly and efficiently remove free dyes from the sample with just a single step and enables an individual or 96 sample to be processed simultaneously in less than 1 or 10 minutes with very little hands-on time. Since the magnetic resin only adsorbs the free dye, primer, dimer, adapter, salt, detergent, dNTPs, and enzyme, the labeled DNA/RNA rate is exceptionally higher than >90%. Moreover, the magnetic beads can remove most of the dyes if the appropriate amount of samples and buffer conditions are used (Table1).
Table 1
Fluorescent Dyes
Binding Capacity
ng /mg beads**
Fluorescent dyes
Binding capacity
ng /mg beads**
Alexa Fluor 546 C5-Maleimide
99.7
Alexa Fluor™ 514 NHS Ester
45.2
Cyanine 3 carboxylic acid
99.1
Cyanine 5 carboxylic acid
49.7
Cyanine 3 amine
99.3
Cyanine 3.5 carboxylic acid
99
Cyanine 5.5 amine
99.8
Cyanine 5.5 carboxylic acid
99.7
Cyanine 5 amine
49.85
Sulfo-Cyanine 5.5 amine
99.9
Sulfo-Cyanine3 amine
93.3
Sulfo-Cyanine5 carboxylic acid
24.9
DyLight™ 488 NHS Ester
90.5
DyLight™ 633 NHS Ester
87.4
Dylight 680-4x PEG NHS Ester
99.8
DyLight™ 405 NHS Ester
99
Oregon Green™ 488 carboxylic acid
84.2
FAM amine, 5-isomer
24.57
Rhodamine 5B amine
99.2
Texas Red™ hydrazide
890
Cibarcron blue F3GA
99.7
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
120.3
Bromocresol purple
105.2
Phenol red
99.5
Denim red
101
Bromophenol blue
99
Denim blue
104.2
102.4
Fluorescent Dyes
Binding Capacity
ng /mg beads**
Alexa Fluor 546 C5-Maleimide
99.7
Alexa Fluor™ 514 NHS Ester
45.2
Cyanine 3 carboxylic acid
99.1
Cyanine 5 carboxylic acid
49.7
Cyanine 3 amine
99.3
Cyanine 3.5 carboxylic acid
99
Cyanine 5.5 amine
99.8
Cyanine 5.5 carboxylic acid
99.7
Cyanine 5 amine
49.85
Sulfo-Cyanine 5.5 amine
99.9
Sulfo-Cyanine3 amine
93.3
Sulfo-Cyanine5 carboxylic acid
24.9
DyLight™ 488 NHS Ester
90.5
DyLight™ 633 NHS Ester
87.4
Dylight 680-4x PEG NHS Ester
99.8
DyLight™ 405 NHS Ester
99
Oregon Green™ 488 carboxylic acid
84.2
FAM amine, 5-isomer
24.57
Rhodamine 5B amine
99.2
Texas Red™ hydrazide
890
Cibarcron blue F3GA
99.7
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
120.3
Bromocresol purple
105.2
Phenol red
99.5
Denim red
101
Bromophenol blue
99
Denim blue
104.2
102.4
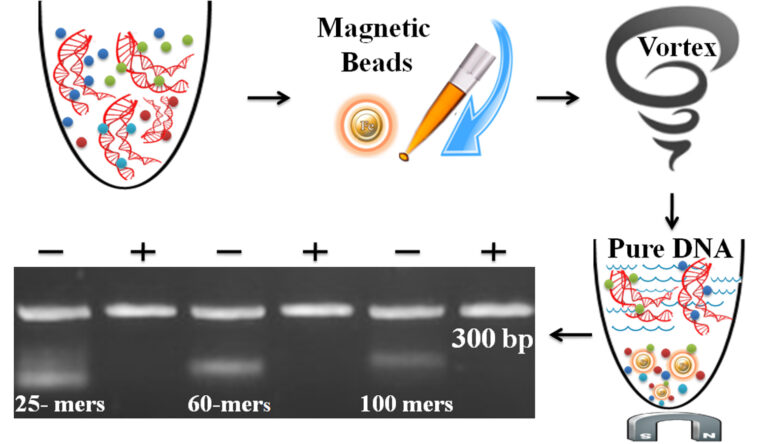
The one-minute dye removal protocol is straightforward.
1.
Add the beads directly to the sample.
2.
Pipette or vortex to capture the free dye.
3.
Magnetic separation of the beads from the protein solution, while the supernatant contains the purified and ready-to-run products.
●
Simple protocol: No liquid transfer, One-tube, One-step
●
Ultrafast: One-minute protocol
●
Higher purity and recovery > 90% DNA
●
●
Cost-effective: Eliminates columns, filters, laborious repeat pipetting, and ethanol
●
High-throughput: Compatible with many different automated liquid handling systems
A. Materials Required by the User
●
18.2 MΩ.cm, DNase/RNase-Free Ultrapure Water
●
Triton™ X-100, Sigma, Catalog No. T8787
●
Others
Item
Magnetic Rack for centrifuge tube
** Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following magnetic Racks
Source
• BcMag™ Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-01)
• BcMag™ Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-02)
• BcMag™ Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-03)
• BcMag™ Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-04)
Item
BcMag™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack.
Source
• BcMa™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack (side-pull) compatible with 96-well PCR plate and 96-well microplate or other compatible Racks (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-05)
Item
Adjustable Single and Multichannel Pipettes
Item
Centrifuge with Swinging Bucket
Addition items are required if using 96-well PCR plates / tubes
Vortex Mixer
** The user can also use other compatible vortex mixers. However, the Time and speed should be optimized, and the mixer should be: Orbit ≥1.5 mm-4 mm, Speed ≥ 2000 rpm
Eppendorf™ MixMate™
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 5353000529
Tube Holder PCR 96
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674005
Tube Holder 1.5/2.0 mL, for 24 × 1.5 mL or 2.0 mL
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674048
Smart Mixer, Multi Shaker
BenchTop Lab Systems, Cat. No. 5353000529
1.5/2.0 mL centrifuge tube
96-well PCR Plates or 8-Strip PCR Tubes
PCR plates/tubes
** IMPORTANT! If using other tubes or PCR plates, make sure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of PCR Tubes or PCR plates must be ≥2.5mm.
Items
Magnetic Rack for centrifuge tube
** Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following magnetic Racks
Source
●
BcMag™ Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-01)
●
BcMag™ Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-02)
●
BcMag™ Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-03)
●
BcMag™ Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-04)
BcMag™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack
●
BcMa™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack (side-pull) compatible with 96-well PCR plate and 96-well microplate or other compatible Racks (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-05)
Adjustable Single and Multichannel Pipettes
Centrifuge with Swinging Bucket
Addition items are required if using 96-well PCR plates/tubes
Vortex Mixer
** The user can also use other compatible vortex mixers. However, the Time and Speed should be optimized, and the mixer should be: Orbit ≥1.5 mm-4 mm, Speed ≥ 2000 rpm
Eppendorf™ MixMate™
Tube Holder PCR 96
Tube Holder 1.5/2.0 mL, for 24 × 1.5 mL or 2.0 mL
Smart Mixer, Multi Shaker
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 5353000529
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674005
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674048
BenchTop Lab Systems, Cat. No. 5353000529
Eppendorf™ MixMate™
Tube Holder PCR 96
Tube Holder 1.5/2.0 mL, for 24 × 1.5 mL or 2.0 mL
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 5353000529
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674005
BenchTop Lab Systems, Cat. No. 5353000529
1.5/2.0 mL centrifuge tube
96-well PCR Plates or 8-Strip PCR Tubes
PCR plates/tubes
! IMPORTANT ! If using other tubes or PCR plates, make sure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of PCR Tubes or PCR plates must be ≥2.5mm.
B. Procedure
! Important !
1.
The following protocol is optimized for the efficient cleanup of 10µl DNA sample. The protocol can be scaled up or down as needed. However, the procedure may need to be optimized if an alternative reaction scale is used.
2.
Shake or vortex the bottle to completely resuspend the magnetic beads before using.
3.
Do not allow the magnetic beads to sit for more than two minutes before dispensing.
4.
Dilute organic solvent to 0.2-0.5% (final) with dH2O if the labeling reaction contains more than 0.5% organic solvent such as DMSO (Dimethyl sulfoxide) in the labeling solution.
5.
Based on applications, the user should choose buffer conditions based on table1. For example, if the sample does not contain detergent, add 1 μL of 1% Triton™ X-100 solution to a 10 μL sample (final concentration is 0.1%).
6.
Quantification of the nucleic acids: Use only fluorescence methods such as qPCR, Qubit, and Pico Green.
Table 1 – DNA Fragment Removal
Table 1 – DNA Fragment Removal
DNA
Buffer
+ 0.1%
Triton x-100
pH7.5
– 0.1%
Triton x-100
pH7.5
+ 0.1%
Triton x-100
pH 8.0
– 0.1%
Triton x-100
pH 8.0
+ 0.1%
Triton x-100
pH 8.8
– 0.1%
Triton x-100
pH 8.8
dsDNA
(100 bp)
No Removal
Removal
Removal
Removal
No Removal
Removal
dsDNA
(150 bp)
No Removal
Removal
No Removal
Removal
No Removal
Removal
dsDNA
(200 bp)
No Removal
Removal
No Removal
Removal
No Removal
Removal
dsDNA
(300 bp)
No Removal
No Removal
No Removal
No Removal
No Removal
No Removal
ssDNA
100 mer
Removal
Removal
Removal
Removal
Removal
Removal
Please Note:
dsDNA – Double-Stranded DNA; ssDNA – Single-Stranded DNA
The assay was done by using the following conditions:
1. 10 mM Tris-HCl with or without 0.1% triton (final concentration) and three different: pH 7.5, pH 8.0 and pH 8.8
1.
Add 5 μL magnetic beads to the 10 μL DNA sample.
2.
If necessary, briefly centrifuge at 2500 rpm for 30 seconds to bring all contents to the bottom of the tube.
3.
Mix thoroughly for 1 minute by slowly pipetting up and down 25 times (one minute) or by vortex mixer for 5 minutes at 2500 rpm.
4.
If necessary, briefly centrifuge at 2500 rpm for 30 seconds to bring all contents to the bottom of the tube.
5.
Place the sample plate on the magnetic separation plate for 30 seconds or until the solution is clear to separate beads from the solution.
6.
Transfer the supernatant to a clean plate while the sample plate remains on the magnetic separation plate for downstream applications.
C. Troubleshooting
Problem
Low DNA Recovery
Probable Cause
Vertexing speed is too fast.
Vertexing time is too long.
Suggestion
Problem
Low DNA Recovery
Probable Cause
Using too many magnetic beads
Suggestion
Thoroughly resuspend the magnetic beads and use the correct amounts of the beads.
Problem
Failure to Remove Impurities.
Probable Cause
Used inappropriate PCR tubes or PCR plates
Suggestion
Make sure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of PCR Tubes or PCR plates is ≥2.5mm.
Problem
Failure to Remove Impurities.
Probable Cause
Vortex speed is too slow, or vortex time needs to be longer.
Suggestion
Problem
Failure to Remove Impurities.
Probable Cause
Using fewer magnetic beads
Suggestion
Thoroughly resuspend the magnetic beads and use the correct amounts of the beads.
Problem
Failure to Remove Impurities.
Probable Cause
Strong secondary structure of DNA fragments ( < 50bp dsDNA or < 100 mer ssDNA)
Suggestion
Denature the sample by heating it at 95°C for 2 min.
Problem
Failure to Remove Impurities.
Probable Cause
Too much primer, dimer, adaptor, free dye, and detergent
Suggestion
Problem
Probable Cause
Suggestion
Low DNA Recovery
Vertexing speed is too fast.
Vertexing time is too long.
Using too many magnetic beads
Thoroughly resuspend the magnetic beads and use the correct amounts of the beads.
Failure to Remove Impurities.
Used inappropriate PCR tubes or PCR plates
Make sure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of PCR Tubes or PCR plates is ≥2.5mm.
Vortex speed is too slow, or vortex time needs to be longer.
Using fewer magnetic beads
Thoroughly resuspend the magnetic beads and use the correct amounts of the beads.
Strong secondary structure of DNA fragments ( < 50bp dsDNA or < 100 mer ssDNA )
Denature the sample by heating it at 95°C for 2 min.
Too much primer, dimer, adaptor, free dye, and detergent
Get the Latest News and Updates by Email
6393 Nancy Ridge Dr. Suite A
San Diego, CA 92121 USA
Fax: +1-858-909-0057
Get the Latest News and Updates by Email
© 2023 Bioclone Inc. All Rights Reserved.