- +1 858 909 0079
- +1 858 909 0057
- [email protected]
- +1 858 909 0079
- [email protected]

Products
Specification
Composition
Silica-enclosed magnetic beads are modified with our proprietary chemistry.
Stability
Short Term (<1 hour): pH 4-11; Long-Term: pH 4-10
Temperature: 4°C -140°C; Most organic solvents
Magnetization
~40-45 EMU/g
Type of Magnetization
Superparamagnetic
Formulation
Storage
Ship at room temperature, Store at 4°C upon receipt.
Detergents contain a hydrophilic head group and a hydrophobic tail. The hydrophobic moiety usually consists of a hydrocarbon chain, while the hydrophilic part has a polar head. Three types of detergents are commonly used in laboratory research, including:
●
Non-ionic detergents contain uncharged hydrophilic head groups such as Triton X-100, Triton X-114, NP-40, Tween-20, and Tween-80.
●
Ionic detergents are comprised of a hydrophobic chain and anionic or cationic head groups such as sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB).
●
Zwitterionic detergents: Those detergents like CHAPS contain negatively and positively charged atomic groups in equal numbers. Therefore, they do not possess a net charge.
Detergents (surfactants) are essential for biomedical research. For successful downstream analysis, it is critical to reduce or entirely remove unbound detergents from the biological sample. However, excess unbound detergent is usually poorly compatible with many downstream applications, including ELISA, protease digestion of proteins, isoelectric focusing, and mass spectrometry (MS). Several commercially available detergent removal methods include prolonged dialysis, anion exchange chromatography, detergent removal spin column, and acetone precipitation. However, these procedures, such as using detergent removal columns, are either laborious or suffer from sample losses and are challenging for low volume samples and high thorough-put automation. We developed a novel, efficient surfactant removal system to overcome these limitations.
BcMag™ One-Step Detergent Removal Kit uses magnetic resin coated with proprietary chemistry to remove detergents. Compared with the detergent removal columns, the resin can quickly and efficiently remove free detergents from the sample with just a single step and enables individual samples or 96 samples to be processed simultaneously in less than 1 minute or 10 minutes with 95% sample recovery. Since the magnetic resin only adsorbs the detergent, the sample recovery rate is exceptional >90%-95%.
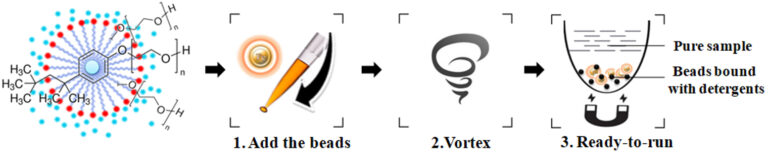
●
Simple protocol: No liquid transfer, One-tube, One-step, and one-minute protocol
●
Easy-to-use
●
Reliable and reproducible results with exceptional >90% recovery for protein (>6 kDa, aprotinin) or DNA/RNA (>25mer dsDNA)
●
Effective Cleanup: Remove 95% free detergent.
●
Cost-effective: Eliminates columns, filters, and laborious repeat pipetting
●
High throughput: Compatible with many different automated liquid handling systems
Materials Required by the User
Item
Magnetic Rack for centrifuge tube
** Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following magnetic Racks
Source
• BcMag™ Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-01)
• BcMag™ Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-02)
• BcMag™ Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-03)
• BcMag™ Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-04)
Item
BcMag™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack.
Source
• BcMa™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack (side-pull) compatible with 96-well PCR plate and 96-well microplate or other compatible Racks (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-05)
Item
Adjustable Single and Multichannel Pipettes
Item
Centrifuge with Swinging Bucket
Addition items are required if using 96-well PCR plates / tubes
Vortex Mixer
** The user can also use other compatible vortex mixers. However, the Time and speed should be optimized, and the mixer should be: Orbit ≥1.5 mm-4 mm, Speed ≥ 2000 rpm
Eppendorf™ MixMate™
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 5353000529
Tube Holder PCR 96
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674005
Tube Holder 1.5/2.0 mL, for 24 × 1.5 mL or 2.0 mL
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674048
Smart Mixer, Multi Shaker
BenchTop Lab Systems, Cat. No. 5353000529
1.5/2.0 mL centrifuge tube
96-well PCR Plates or 8-Strip PCR Tubes
PCR plates/tubes
** IMPORTANT! If using other tubes or PCR plates, make sure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of PCR Tubes or PCR plates must be ≥2.5mm.
Items
Magnetic Rack for centrifuge tube
** Based on sample volume, the user can choose one of the following magnetic Racks
Source
●
BcMag™ Rack-2 for holding two individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-01)
●
BcMag™ Rack-6 for holding six individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-02)
●
BcMag™ Rack-24 for holding twenty-four individual 1.5-2.0 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-03)
●
BcMag™ Rack-50 for holding one 50 ml centrifuge tube, one 15 ml centrifuge tube, and four individual 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-04)
BcMag™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack
●
BcMa™ 96-well Plate Magnetic Rack (side-pull) compatible with 96-well PCR plate and 96-well microplate or other compatible Racks (Bioclone, Cat. No. MS-05)
Adjustable Single and Multichannel Pipettes
Centrifuge with Swinging Bucket
Addition items are required if using 96-well PCR plates/tubes
Vortex Mixer
** The user can also use other compatible vortex mixers. However, the Time and Speed should be optimized, and the mixer should be: Orbit ≥1.5 mm-4 mm, Speed ≥ 2000 rpm
Eppendorf™ MixMate™
Tube Holder PCR 96
Tube Holder 1.5/2.0 mL, for 24 × 1.5 mL or 2.0 mL
Smart Mixer, Multi Shaker
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 5353000529
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674005
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674048
BenchTop Lab Systems, Cat. No. 5353000529
Eppendorf™ MixMate™
Tube Holder PCR 96
Tube Holder 1.5/2.0 mL, for 24 × 1.5 mL or 2.0 mL
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 5353000529
Eppendorf, Cat. No. 022674005
BenchTop Lab Systems, Cat. No. 5353000529
1.5/2.0 mL centrifuge tube
96-well PCR Plates or 8-Strip PCR Tubes
PCR Plates/Tubes
! IMPORTANT ! If using other tubes or PCR plates, ensure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of PCR Tubes or PCR plates must be ≥2.5mm.
Procedure
! IMPORTANT !
●
The following protocol is an example. The beads and sample volume can be rational Scale-up (or down). Do not use buffers containing organic solvents.
●
The user should optimize the beads and detergent concentration ratio based on the binding capacity listed in Table 1.
Detergent
Binding Capacity**
Protein Recovery (%)
Triton* X-100
17 μg/mg beads
>97
Triton X-114
16.5 μg/mg beads
>96
Tween-20
9 μg/mg beads
>92
NP-40
16 μg/mg beads
>96
Brij-35
16 μg/mg beads
>94
Tween-80
16 μg/mg beads
>93
DDM
15 μg/mg beads
>93
CY-6
16.5 μg/mg beads
>97
CTAB
10 μg/mg beads
>60
** Binding capacity assay condition: Mix with 10 μl magnetic beads (100 mg/ml) with 100 μl protein sample (1:400 dilution of Human serum) containing detergents in 0.1M Sodium phosphate, 0.15M NaCl, pH7.5 buffer, and vortex at 2000 rpm for 5 minutes)
Procedure
1.
Shake the bottle to resuspend the Magnetic beads until it is homogeneous entirely.
! IMPORTANT !
It is essential to mix the beads before dispensing. Do not allow the beads to sit for more than 2 minutes before dispensing. Resuspend the magnetic beads every 2 minutes.
2.
Add an appropriate amount of the magnetic beads to the sample containing free detergent. Mix the sample with beads for 1-2 minutes by slowly pipetting up and down 20-25 times or vortex for 5 minutes at 2000 rpm for PCR plates or 800 rpm for microplates.
! IMPORTANT !
3.
Place the sample plate or tube on the magnetic separation plate for 30 seconds or until the solution is clear.
4.
Transfer the supernatant to a clean plate/tube while the sample plate remains on the magnetic separation plate. The sample is ready for downstream applications.
C. Troubleshooting
Problem
Low Protein Recovery
Probable Cause
Vortexing time is too long.
Suggestion
If using other digital vortex mixers, the vortex condition such as speed and time has to be optimized.
Problem
Low Protein Recovery
Probable Cause
Using too many magnetic beads
Suggestion
Completely resuspend the magnetic beads and reduce the amounts of the beads.
Problem
Failure to remove detergent.
Probable Cause
Used inappropriate tubes or plates
Suggestion
Ensure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of the Tubes or well of the plate is ≥2.5mm.
Problem
Failure to remove detergent.
Probable Cause
Vortex speed is too slow, or vortex time is too short.
Containing too much detergent in the sample
Suggestion
Problem
Probable Cause
Suggestion
Low Protein Recovery
Vortexing time is too long.
If using other digital vortex mixers, the vortex condition such as speed and time has to be optimized.
Using too many magnetic beads
Completely resuspend the magnetic beads and reduce the amounts of the beads.
Failure to remove detergent
Used inappropriate tubes or plates
Ensure that the well diameter at the bottom of the conical section of the Tubes or well of the plate is ≥2.5mm.
1.
Ilavenil, S., Al-Dhabi, N.A., Srigopalram, S. et al. Removal of SDS from biological protein digests for proteomic analysis by mass spectrometry. Proteome Sci 14, 11 (2016).
2.
Puchades M, Westman A, Blennow K, Davidsson P. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from protein samples before matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1999;13(5):344-9.
3.
Yeung YG, Nieves E, Angeletti RH, Stanley ER. Removal of detergents from protein digests for mass spectrometry analysis. Anal Biochem. 2008;382(2):135-137
4.
Antharavally BS, Mallia KA, Rosenblatt MM, Salunkhe AM, Rogers JC, Haney P, Haghdoost N. Efficient removal of detergents from proteins and peptides in a spin column format. Anal Biochem. 2011 Sep 1;416(1):39-44.
5.
W. Holloway. A simple procedure for removal of Triton X-100 from protein samples, Analytical Biochemistry, Volume 53, Issue 1,1973, Pages 304-308.
6.
Stetsenko, A.; Guskov, A. An Overview of the Top Ten Detergents Used for Membrane Protein Crystallization. Crystals 2017
Get the Latest News and Updates by Email
6393 Nancy Ridge Dr. Suite A
San Diego, CA 92121 USA
Fax: +1-858-909-0057
Get the Latest News and Updates by Email
© 2023 Bioclone Inc. All Rights Reserved.